Patient Care Delivery Under Scanner: Special Needs
The term “special needs” is a catch-all phrase which can refer to a vast array of diagnoses and/or disabilities in individuals. These conditions develop from a combination of genetic, nongenetic and environmental influences.
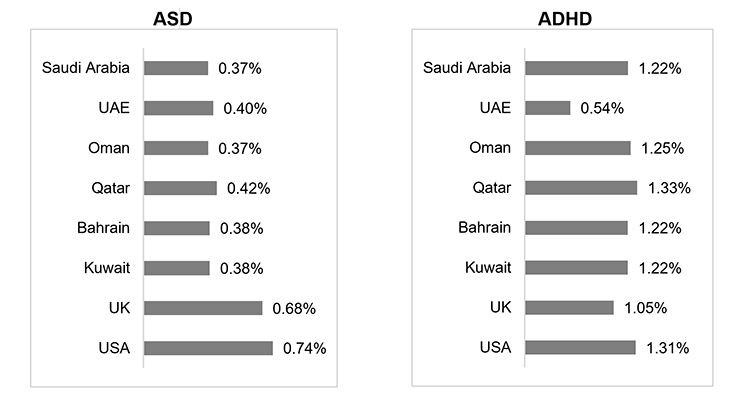
The estimated prevalence of Autism and ADHD in the GCC countries is comparable/ lower than UK, US, but there is significant under reporting due to poor diagnosis.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are the most common neurological disorders in the special needs category. As per WHO, 1 in 160 children (~62.5 per 10,000) worldwide have ASD. Also, the prevalence of ADHD in children is estimated to be 7.2%.
As per available stats, the estimated prevalence of Autism and ADHD in the GCC countries is comparable/ lower than UK, US, but there is significant under reporting due to poor diagnosis.
Age-standardized prevalence (% of total population, 2017)1
1 IHME, Global burden of diseases
Looking for more insights? Never miss an update.
The latest news, insights and opportunities from global commercial real estate markets straight to your inbox.
For the most part cases are underreported due to shortage of care facilities and specialists to diagnose properly. In other cases, it results from a lack of parents’ awareness to recognize symptoms, seek diagnostic clarification, and accept the child’s condition.
The exhibit outlines key disorders leading to various forms for disability. They have been analyzed in terms of the type of disability, and support needed, which is broadly classified as:
- Medical services: Continuous clinical care required in the form of inpatient and / or long term care (e.g., traumatic brain injury cases)
- Allied health services: Support in the form of physical therapy, speech therapy and occupational therapy etc.
Most disorders require a combination of medical and allied health services with a varying mix as per severity level. Severe and profound disorders require a high level of medical care. Moreover, the likelihood of receiving education is also dependent on the type of disorder as well as severity of each disorder.
Typically, the patient pathway of individuals with special needs involves receiving a diagnostic report, which foreshadows the services that are needed and a basic “road map” as to where to receive those services. The parents then choose the facility, where further assessment is done, and services are provided.
Various operating models of the Child Rehabilitation Segment in the GCC are as follows-
- Clinics / Centres: Outpatient services provide rehabilitation including diagnosis, speech therapy, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, educational support, behavioral therapy, and other related services.
- Day Care Programs: Operational focus is on children with severe disability who attend the rehabilitation programs, operating for a whole year targeted to achieve a better quality of life.
- Special Needs Education: Catering to the student segment who have special educational needs due to severe learning difficulties, physical disabilities, or behavioral problems.
Insurance coverage for Special Needs
Recent changes to insurance coverage in many GCC countries have increased the annual limit for rehabilitation claims, based on the insurance class. Rehabilitation services are usually offered in bundles, such as defined therapy sessions, with extra sessions subject to further approvals. Increase in limit for insurance coverage has widened the market for medical centres and day centres. These facilities must incorporate with insurance networks to receive insured patients and cater to this market.
Ensuring Adequate Centres in the GCC
JLL Healthcare has analyzed the required relevant special needs centres in the GCC in terms of the type of disability caused, and support needed. For the purpose of this analysis, only selected disorders which can be catered to in a centre set up (without inpatient facilities) have been considered. As per estimates, 3,500 - 4,000 special need centres are required to cater to the mildly disabled pediatric population across GCC, considering an average of 100 children per center. Also, this translates to the need of 2.4 Million sq ft of BUA (considering 600-700 sq ft BUA per center as per market benchmarks). It is to be noted that this is mainly for mild cases for selected disorders. Severe / extreme cases may only benefit from inpatient stay. The spectrum of services in these centres include educational support, speech therapy, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, behavioral therapy, etc.
General outlook of the child rehabilitation market in the region
Currently, there is an undersupply of facilities and personnel in the child rehabilitation market. Other factors impacting the sector include lack of child-centric approach, insufficient monitoring, lack of focus on Occupational Therapy as well as lack of research / empirical based care.
The WHO estimates that the burden of disability and special needs is rising with 80% of children with special needs are not receiving education or the rehabilitation services that they need. Going further, keeping in mind factors such as increasing population, awareness and advancement in treatment methods etc, there is a need to provide for more centres in the GCC, especially ones that offer private facilities to ensure ease of access for individuals and families.